Given the root of a binary tree, find the maximum value v for which there exist different nodes a and b where v = |a.val - b.val| and a is an ancestor of b.
A node a is an ancestor of b if either: any child of a is equal to b or any child of a is an ancestor of b.
Example 1:
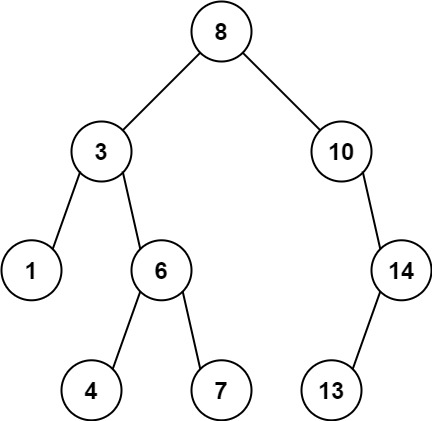
Input: root = [8,3,10,1,6,null,14,null,null,4,7,13]
Output: 7
Explanation: We have various ancestor-node differences, some of which are given below :
|8 - 3| = 5
|3 - 7| = 4
|8 - 1| = 7
|10 - 13| = 3
Among all possible differences, the maximum value of 7 is obtained by |8 - 1| = 7.
Example 2:
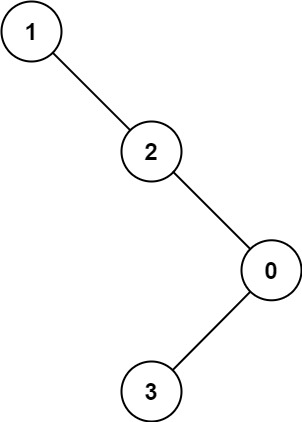
Input: root = [1,null,2,null,0,3]
Output: 3
Constraints:
The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[2, 5000].0 <= Node.val <= 10<sup>5</sup>
Solution
class Solution(object):
def maxAncestorDiff(self, root)->int:
return self.helper(root, root.val, root.val)
def helper(self, r, mn, mx):
if not r:
return mx - mn
mn = min(mn, r.val)
mx = max(mx, r.val)
left_diff = self.helper(r.left, mn, mx)
right_diff = self.helper(r.right, mn, mx)
return max(left_diff, right_diff)
Second
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class TreeNode:
def __init__(self, x):
self.val = x
self.left = self.right = None
class Solution:
def maxAncestorDiff(self, root) :
m=[0]
self.dfs(root,m)
return m[0]
def dfs(self, root, m):
if not root:
return float('inf'), float('-inf')
left = self.dfs(root.left, m)
right = self.dfs(root.right, m)
min_val = min(root.val, min(left[0], right[0]))
max_val = max(root.val, max(left[1], right[1]))
m[0] = max(m[0], max(abs(min_val - root.val), abs(max_val - root.val)))
return min_val, max_val

